
The actual key to encrypt and decrypt the data is stored in the CKDS (“Cryptographic Key Data Set”). Note that, after encryption has been enabled for a tablespace or index, the next Reorg of the object will encrypt the data. The second can be used for image copies and utility work files as early as Db2 11, but will be made available through DDL for Db2 data only in Db2 12 (as part of Function Level 502). The first and third methods of enabling encryption for Db2 datasets are supported in both Db2 11 and 12.
WHAT IS DISK UTILITY ENCRYPTION ARCHIVE
You can also choose to encrypt the BSDS, active logs, archive logs (on disk), image copies, and utility work files. Tablespaces or indexes, or both, can be encrypted the Db2 catalog and directory can be encrypted, as well as user data. So, it is true that you need a z14 for acceptable performance of encryption (more on performance below).īecause encryption and decryption are done at I/O time, they are almost completely “transparent” to Db2. This is not true, but the Crypto 6-S processor is much faster than the Crypto 5-S, and the 6-S is available only on a z14.

There is a misconception that a z14 is necessary to implement encryption. You will need the attached Crypto processor. SMS encryption is available in z/OS 2.2 (if the PTF for APAR OA50569 has been applied) or z/OS 2.3. To be encrypted, a dataset must have the Extended attribute. z/OS allows three methods of enabling encryption in priority order, these are: in a RACF dataset profile, as an attribute of the dataset (specified in JCL with DSKEYBL syntax or KEYLABEL in IDCAMS), and as an attribute in a SMS DATACLAS. It is worth pointing out that this encryption technique does not support tape. IBM decided to implement the feature in the media manager, which is a low-level access mechanism (part of DFSMS) used by BSAM, QSAM, VSAM, and by Db2. Encryption exploits a hardware instruction which is executed in an attached Crypto processor, to minimize the cost of the instruction. For Db2 12, there is additional function, which has been provided via Continuous Delivery as part of Function Level 502.įirst, let’s look at the encryption mechanism itself, how it is implemented, and what you will need to deploy it. TDE has been provided for both Db2 11 and Db2 12. Transparent Data Encryption provides a mechanism to encrypt your data at rest, on disk. IBM has provided a partial solution in Transparent Data EncryptionTM (or “TDE”) for Db2, which is part of a wider effort they call zSystem Pervasive EncryptionTM (or “zSPE”). None of us want the cost, potential fines, or negative publicity associated with a potential or real data exposure. Your auditors, internal and external, may be demanding action to protect your valuable Db2 data from prying eyes. As a Db2 DBA, one of your responsibilities is the protection of the data your business needs to run. Hardware-based encryption is also beneficial because it can be turned on indefinitely, meaning that the user does not have to remember to turn it on when required.There have been several high visibility data exposures in the news over the last year or so. This adds further security against potential threats posed by attackers who can access the computer memory. Hardware-based disk encryption generates and stores encryption keys and user information within the drive hardware therefore, this information is held independently from the operating system and the software.
WHAT IS DISK UTILITY ENCRYPTION FULL
The master boot record can be encrypted as well if a hardware-based full disk encryption is used. Since full disk encryption is usually software-based, it often excludes the master boot record, which is the first subdivided track of the hard disk. Full disk encryption will encrypt operating system files as well as temporary files, or basically, any and all files found on the disk that is being encrypted. The goal of encrypting data is to prevent unwanted users from accessing the data stored on the drives of a computer.
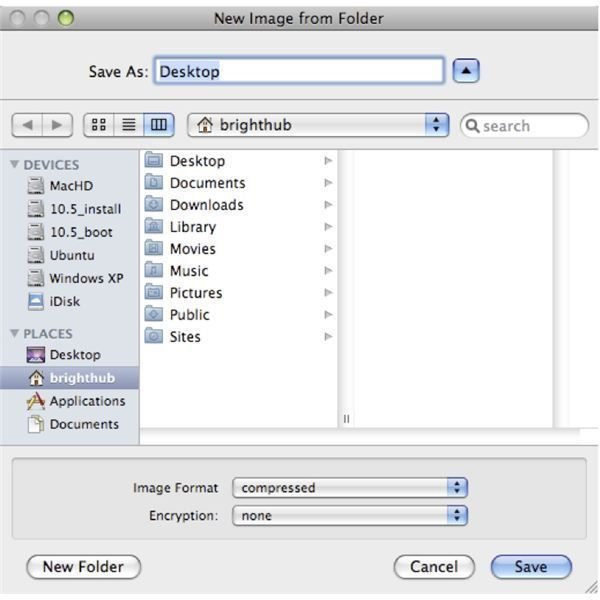
Encryption scrambles the contents of a message or file so that it can only be read by someone who has access to the encryption key, which will unscramble the file.
Partitions are used by some computer users as a way of dividing the storage space of a hard drive.
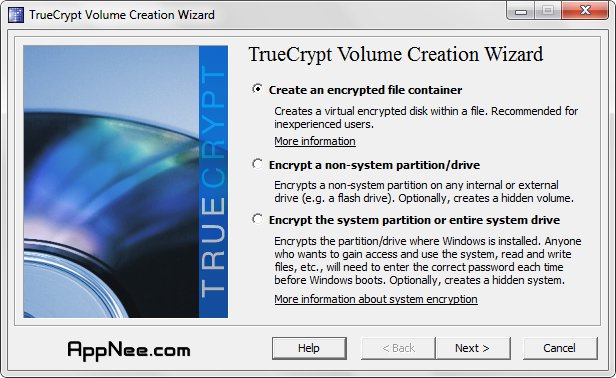
Full disk encryption is the encoding of data that is placed on a disk, including programs that encrypt partitions on the operating systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
